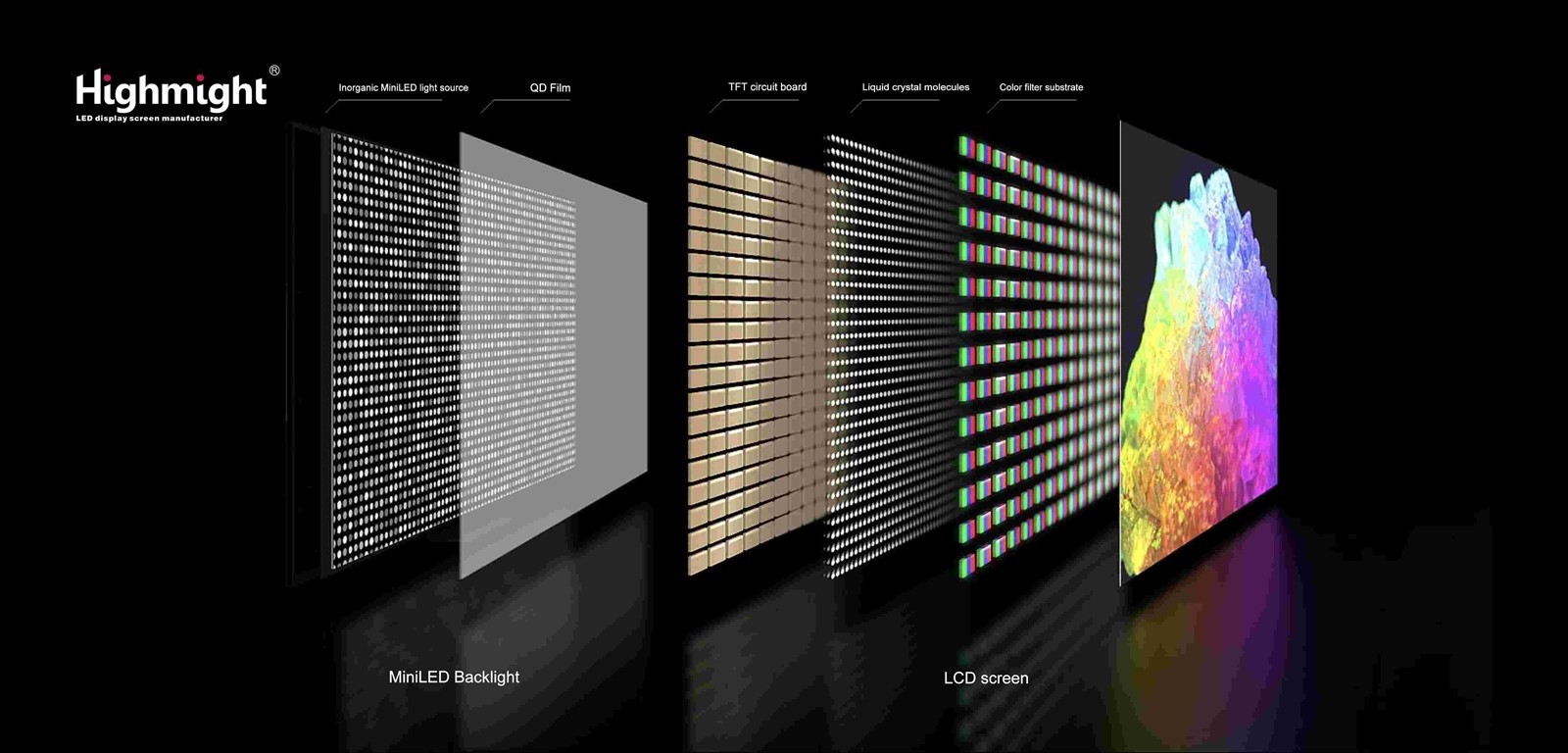
Advantages of LCD screens:
(1) Mature technology and low cost: especially in large-size areas (TVs, monitors), it has high cost-effectiveness and lower maintenance costs.
(2) No screen burn-in problem: suitable for long-term display of fixed content (such as monitoring screens, digital signage).
(3) DC dimming eye protection: the backlight is always on, the brightness is controlled by adjusting the current, and there is no flicker at low brightness, which is suitable for sensitive users
(4) High brightness performance: high-end LCDs (such as Mini-LED+ backlight) can achieve ultra-high brightness (above 1000 nits), suitable for HDR and outdoor use.
Disadvantages of LCD screens:
(1) Limited contrast: the backlight cannot be completely turned off, black appears gray, and dark field details are weak.
(2) Thickness and weight: the backlight layer and liquid crystal layer make the body thicker, making it difficult to achieve flexible folding design.
(3) Slow response speed: it takes several milliseconds for the liquid crystal molecules to turn, and fast images may have ghosting (IPS panel+ has improved).
(4) Backlight uniformity problem: light leakage may occur at the edges, affecting the dark field landscape.
Advantages of OLED screens
(1) Ultra-high contrast and pure black performance: OLED pixels can be turned off independently to achieve high contrast, black areas are completely non-luminous, and the picture has a strong sense of layering, which is especially suitable for dark film and television content.
(2) Thinner, lighter, and more flexible: No backlight layer is required, the structure is simple, and the screen can be ultra-thin and flexible (such as folding screens and curved screens).
(3) Wide viewing angle and color performance: Nearly 180-degree viewing angle, no color deviation when viewed from the side, higher color saturation, and strong visual impact.
(4) Fast response speed (microsecond level): Almost no ghosting, suitable for games, high-speed sports pictures, and smoother dynamic display.
(5) Flexible power consumption: When displaying dark or black pictures, turning off pixels can save power, but all-white pictures may consume more power than LCD.
Disadvantages of OLED screens:
(1) Burn-in risk: Organic materials have a limited lifespan, and long-term display of static content may cause afterimages
(2) Brightness and life limit: High brightness is prone to accelerated aging, especially for blue pixels. Outdoor peak brightness and lifespan have been significantly optimized by viewing layer devices.
(3) PWM dimming + strobe: The brightness is adjusted by strobe at low brightness, and sensitive users may feel eye fatigue (some models support DC dimming to alleviate this).
(4) High cost: The manufacturing process is complex and is currently mainly used for small sizes. The price of large-size screens (such as TVs) is significantly higher than that of LCDs. Currently, large-size OLED TVs are mainly manufactured by Samsung and LG.
Advantages of Micro LED screens:
(1) High brightness and wide color gamut: Micro LED uses inorganic materials, and the brightness of a single pixel far exceeds that of OLED, easily reaching more than 2000 nits, which is suitable for HDR content and outdoor scenes. The color gamut covers a wider range and the color reproduction is accurate. Currently, research is being conducted on large-size applications of Micro LED, automotive display applications (HUD, PHUD, ARHUD), transparent windows, etc.
(2) High contrast: Each pixel switches independently, and when turned off, it is completely dark, achieving true black with high contrast
3) Low power consumption design: No backlight module, the pixels are powered off under black screen, and the energy consumption is significantly lower than LCD, which is equivalent to or lower than OLED. High-brightness Micro LED power consumption will also be very high, and research is needed on how to reduce power consumption).
(4) Long life of inorganic materials: No aging problem of organic materials, avoiding the burn-in phenomenon of OLED, and the life span can reach more than 100,000 hours.
(5) Ultra-fast response speed: Nanosecond response time, eliminating motion blur, suitable for high-speed scenes such as e-sports and VR.
(6) Wide viewing angle and high stability: wide viewing angle without color shift, high temperature resistance, impact resistance, and adaptability to harsh environments.
(7) Modular design: supports seamless splicing, can be customized to any size and shape, suitable for large-size TVs, cinemas, advertising screens and other different scenarios.
(8) Thin and flexible: glass-based backplane or flexible backplane is feasible.
Disadvantages of Micro LED screens:
(1) Manufacturing difficulties: Mass transfer bonding + and repair technology: millions to tens of millions of micron-level LED chips need to be accurately transferred to the substrate, with an accuracy requirement of +0.5um, low yield and high equipment cost. High repair cost: single chip defects require laser repair or replacement, and the cost of large-screen repair increases sharply (currently there are many mass transfer routes, different companies have different routes, and there is uncertainty in mass production process technology).
(2) Cost and mass production bottleneck: high production cost, the current price of a 65-inch Micro LED TV exceeds one million yuan, the industrial chain is not mature, and the cost of materials and processes remains high. Large-size mass production is difficult, the number of chips increases exponentially with the screen size, and the yield control is difficult, which restricts the commercialization process (materials, equipment, processes and the entire supply chain are not yet mature and there are constraints)
(3) Insufficient technical maturity: the driving circuit is complex, the circuit design is difficult, and it is easy to cause heat dissipation and signal interference problems. Color uniformity challenge: miniaturization makes it difficult to control wavelength consistency, which affects color uniformity and requires complex calibration (LED chip technology, backplane circuit technology, driver chip, etc. all have difficulties).
(4) Market popularization barriers: application scenarios are limited, and in the short term, it is mainly aimed at the high-end commercial market. The popularization of consumer-grade products depends on a significant reduction in costs. The industrial chain is imperfect, from epitaxial growth to transfer bonding repair, as well as detection, packaging, and light control structure, each link has not yet been standardized, and large-scale production lacks supporting support.














